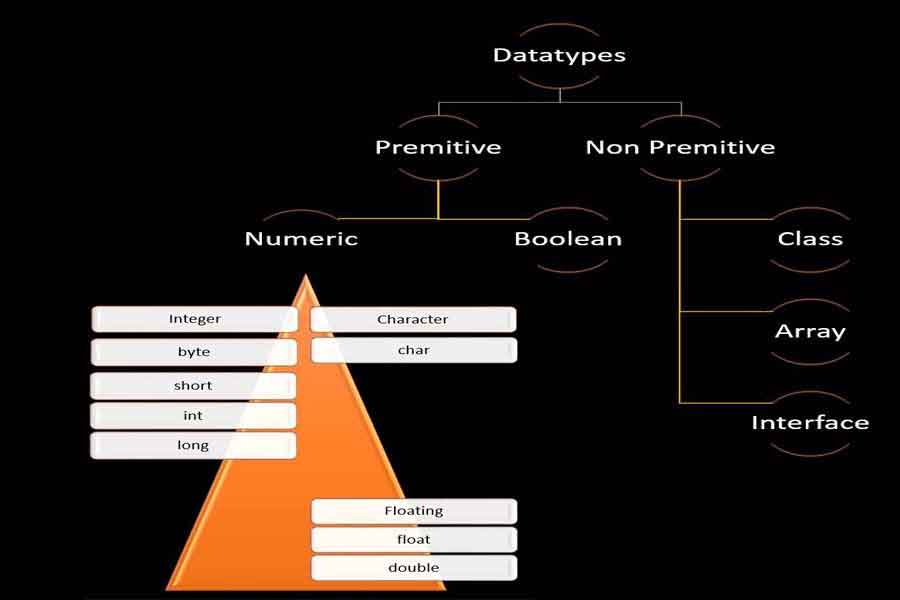
Primitive Datatype
A primitive type is predefined by the language and is named by a reserved keyword.
Non Primitive Datatype
A non primitive type is defined by the user and is named as Class, Array and Interface.
byte
Byte data type is an 8-bit signed two's complement integer.
Minimum value is -128 (-2^7)
Maximum value is 127 (inclusive)(2^7 -1)
Default value is 0
Byte data type is used to save space in large arrays, mainly in place of integers, since a byte is four times smaller than an int.
Example: byte a = 100 , byte b = -50
short
Short data type is a 16-bit signed two's complement integer.
Minimum value is -32,768 (-2^15)
Maximum value is 32,767 (inclusive) (2^15 -1)
Short data type can also be used to save memory as byte data type. A short is 2 times smaller than an int
Default value is 0.
Example: short s = 10000, short r = -20000
int
Int data type is a 32-bit signed two's complement integer.
Minimum value is - 2,147,483,648.(-2^31)
Maximum value is 2,147,483,647(inclusive).(2^31 -1)
Int is generally used as the default data type for integral values unless there is a concern about memory.
The default value is 0.
Example: int a = 100000, int b = -200000
long
Long data type is a 64-bit signed two's complement integer.
Minimum value is -9,223,372,036,854,775,808.(-2^63)
Maximum value is 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 (inclusive). (2^63 -1)
This type is used when a wider range than int is needed.
Default value is 0L.
Example: long a = 100000L, int b = -200000L
float
Float data type is a single-precision 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point.
Float is mainly used to save memory in large arrays of floating point numbers.
Default value is 0.0f.
Float data type is never used for precise values such as currency.
Example: float f1 = 234.5f
double
double data type is a double-precision 64-bit IEEE 754 floating point.
This data type is generally used as the default data type for decimal values, generally the default choice.
Double data type should never be used for precise values such as currency.
Default value is 0.0d.
Example: double d1 = 123.4
boolean
boolean data type represents one bit of information.
There are only two possible values: true and false.
This data type is used for simple flags that track true/false conditions.
Default value is false.
Example: boolean one = true
char
char data type is a single 16-bit Unicode character.
Minimum value is '\u0000' (or 0).
Maximum value is '\uffff' (or 65,535 inclusive).
Char data type is used to store any character.
Example: char letterA ='A'

